Income Tax - Tax Calculation
Verified 17 April 2024 - Directorate for Legal and Administrative Information (Prime Minister)
Want to know how your income tax is calculated? The gross tax is calculated on the basis of a progressive scale. This amount is adjusted (cap, discount) to determine the net tax payable. To calculate your tax, you can use the online simulator. You can also calculate your tax amount yourself, in stages. We'll tell you what you need to know.
To calculate the amount of your tax, you can use the calculation simulator:
2024 Simulator: 2023 Income Tax
You can also consult the online tax return brochure and the tax return explanatory note.
These documents contain a form for calculating the tax amount.
Step-by-step approach
You need to list your income by category and add it up, including:
- Taxable Net Salary
- Pensions, pensions
- Benefits: industrial and commercial (BIC) non-commercial (BNC) or agricultural (BA)
- Land income
- Real estate gains
Warning
Some have to be applied deductions on such income, in particular professional expenses.
Example :
A single person has no income other than his salary and declares €30,000 of taxable net salary.
If he chooses the lump-sum deduction for professional expenses of 10%, its total gross income shall be:
€30,000 - (€30,000 x 10%) = €27,000.
Overall net income = total gross income - deductible expenses
Deductible expenses include:
Taxable net income = total net income - special allowances
These deductions special concerns in particular the elderly or disabled persons.
You may also be affected if you attach your child to your tax home married or in charge of the family.
Répondez aux questions successives et les réponses s’afficheront automatiquement
You are 65 years of age or older
You must have 65 years or older as of december 31, 2023:
- If your income is less than €17,200, you are entitled to a reduction of €2,746.
- If your income is between €17,200 and €27,670, you are entitled to a reduction of €1,373.
This allowance may be doubled if 2 members of the household meet the age requirement.
This abatement cannot be accumulated with the special allowance for the disabled.
You're disabled
If you are disabled, you can benefit from the following:
- If your income is less than €17,200, you are entitled to a reduction of €2,746.
- If your income is between €17,200 and €27,670, you are entitled to a reduction of €1,373.
This abatement cannot be accumulated with the special allowance for the elderly.
You are affected if you have any of the following benefits:
- Military disability pension for a disability of at least 40%
- Accident at work Disability pension for 40%
- Mobility Inclusion Card marked with ‘Disability’
You reattach your child who is married, past or in charge of family
You receive a rebate of €6,674 if you belong to your tax household:
- Your child who is married or a partner of a Civil partnership, with or without children
- Or your child in charge of the family.
Your child (or his or her married or former spouse) must meet one of the following conditions:
- Under 21 years of age
- Be under 25 years of age if pursuing an education
- Perform national service regardless of age
Vous avez choisi
Choisissez votre cas
You are 65 years of age or older
You must have 65 years or older as of december 31, 2023:
- If your income is less than €17,200, you are entitled to a reduction of €2,746.
- If your income is between €17,200 and €27,670, you are entitled to a reduction of €1,373.
This allowance may be doubled if 2 members of the household meet the age requirement.
This abatement cannot be accumulated with the special allowance for the disabled.
You're disabled
If you are disabled, you can benefit from the following:
- If your income is less than €17,200, you are entitled to a reduction of €2,746.
- If your income is between €17,200 and €27,670, you are entitled to a reduction of €1,373.
This abatement cannot be accumulated with the special allowance for the elderly.
You are affected if you have any of the following benefits:
- Military disability pension for a disability of at least 40%
- Accident at work Disability pension for 40%
- Mobility Inclusion Card marked with ‘Disability’
You reattach your child who is married, past or in charge of family
You receive a rebate of €6,674 if you belong to your tax household:
- Your child who is married or a partner of a Civil partnership, with or without children
- Or your child in charge of the family.
Your child (or his or her married or former spouse) must meet one of the following conditions:
- Under 21 years of age
- Be under 25 years of age if pursuing an education
- Perform national service regardless of age
The determination of the gross tax takes place in several successive stages.
Determine the number of tax shares
The number of shares to which you are entitled depends on your situation:
It also takes into account your dependants:
Calculate family quotient
Family Quotient = taxable net income / number of tax shares of the household
Example :
A couple is entitled to 2 shares. If his net taxable income is €30,000, its family quotient will be: €30,000 / 2 = €15,000.
Apply Schedule
The scale is applied to the family quotient obtained.
This scale comprises several tranches.
Income brackets | Income tax bracket rate |
|---|---|
Up to €11,294 | 0% |
From €11,295 to €28,797 | 11% |
From €28,798 to €82,341 | 30% |
From €82,342 to €177,106 | 41% |
More than €177,106 | 45% |
The marginal tax rate (TMI) is the tax rate that applies to the highest tranche of your income.
The average tax rate is the average rate at which your income is taxed. It tells you the how much your tax represents in your income.
Please note
The child tax benefit is limited. It's the family quotient ceiling.
Here are some examples of the calculations:
Répondez aux questions successives et les réponses s’afficheront automatiquement
For a single man
One unmarried (household of a single share) whose net taxable income is €30,000, without any reduction or deduction.
His family quotient is €30,000.
For the calculation of his tax:
- Up to €11,294 : 0%
- From €11,295 to €28,797 : (€28,797 - €11,294) × 11% = €17,503 × 11% = €1,925.33
- From €28,798 to €30,000 : (€30,000 - €28,797) x 30% = €1,203 × 30% = €360.90
Its gross tax is: €0 + €1,925.33 + €360.90 = €2,286.23.
The marginal tax rate (BIT) of this taxpayer is 30%, because its family quotient puts it in that range. But not all his income is taxed to 30%.
For a married couple or a past couple without children
Taxable net income of €60,000
One married couple or former couple without children (household of 2 units) having received taxable net income of €60,000.
His family quotient is €60,000 : 2 = €30,000.
For the calculation of his tax:
- Up to €11,294 : 0%
- From €11,295 to €28,797 : (€28,797 - €11,294) × 11% = €17,503 × 11% = €1,925.33
- From €28,798 to €30,000 : (€30,000 - €28,797) x 30% = €1,203 × 30% = €360.90
The gross tax for each member of the couple is: €0 + €1,925.33 + €360.90 = €2,286.23.
This tax must be multiplied by the number of shares in the tax household. In this example, it will be multiplied by 2 since it is a married or a former couple.
The couple will therefore have to pay a tax of €2,286.23 × 2, or €4,572.46.
The marginal tax rate (IMR.) for this couple is 30%, because its family quotient puts it in that range. But not all his income is taxed to 30%.
Taxable net income of €90,000
One married couple or former couple without children (household of 2 units) having received taxable net income of €90,000.
His family quotient is €90,000 : 2 = €45,000.
For the calculation of his tax:
- Up to €11,294 : 0%
- From €11,295 to €28,797 : (€28,797 - €11,294) × 11% = €17,503 × 11% = €1,925.33
- From €28,798 to €45,000 : (€45,000 - €28,797) x 30% = €16,203 × 30% = €4,860.90
The gross tax for each member of the couple is: €0 + €1,925.33 + €4,860.90 = €6,786.23.
This tax must be multiplied by the number of shares in the tax household. In this example, it will be multiplied by 2 since it is a married or a former couple.
The couple will therefore have to pay a tax of €6,786.23 × 2, or €13,572.46.
The marginal tax rate (IMR.) for this couple is 30%, because its family quotient puts it in that range. But not all his income is taxed to 30%.
For a married or spent couple with 2 children
Taxable net income of €60,000
One married or past couple with 2 children (focus of 3 shares, 1 share for each parent and 1 half share for each child) who received net taxable income of €60,000.
His family quotient is €60,000 : 3 = €20,000.
For the calculation of his tax:
- Up to €11,294 : 0%
- From €11,295 to €20,000 : (€20,000 - €11,294) x 11% = €8,706× 11% = €957.66
This tax must be multiplied by the number of shares in the tax household. In this example, it will be multiplied by 3 since it is a married or past couple with 2 children.
The couple with 2 children should therefore pay a tax of: €957.66 x 3, or €2,872.98
The couple shall be entitled to a maximum tax advantage of €3,518 (€1,759 x 2) for his 2 children (it is the family quotient ceiling).
A married or non-married couple who have received a net taxable income of €60,000 will have to pay a tax of €4,572.46.
The advantage associated with the 2 children is therefore €1,699.48 (€4,572.46 - €2,872.98).
The amount of this benefit shall be less than the maximum benefit of €3,518.
The couple with 2 children will therefore have to pay a tax of €2,872.98
The marginal tax rate (BIT) for this couple with 2 children is 11%, because its family quotient puts it in that range. But not all his income is taxed to 11%.
Taxable net income of €90,000
One married or past couple with 2 children (focus of 3 shares, 1 share for each parent and 1 half share for each child) who received net taxable income of €90,000.
His family quotient is €90,000 : 3 = €30,000.
For the calculation of his tax:
- Up to €11,294 : 0%
- From €11,295 to €28,797 : (€28,797 - €11,294) × 11% = €17,503 × 11% = €1,925.33
- From €28,798 to €30,000 : (€30,000 - €28,797) x 30% = €1,203 × 30% = €360.90
The gross tax for each member of the couple is: €0 + €1,925.33 + €360.90 = €2,286.23.
This tax must be multiplied by the number of shares in the tax household. In this example, it will be multiplied by 3 since it is a married or past couple with 2 children.
The couple with 2 children should therefore pay a tax of €2,286.23 × 3, or €6,858.69.
The couple shall be entitled to a maximum tax advantage of €3,518 (€1,759 x 2) for his 2 children (it is the family quotient ceiling).
A married or non-married couple who have received a net taxable income of €90,000 will have to pay a tax of €13,572.46.
The advantage related to children is €6,713.77 (€13,572.46 - €6,858.69).
This amount exceeds the maximum tax benefit to which the couple is entitled for their 2 children of €3,195.77 (€6,713.77 - €3,518).
The couple with 2 children will therefore have to pay a tax of €10,054.46 (€6,858.69 + €3,195.77).
The marginal tax rate (BIT) for this couple with 2 children is 30%, because its family quotient puts it in that range. But not all his income is taxed to 30%.
For a single parent with 2 children
One single parent with 2 children (household of 2.5 shares, 1 share for the parent, 1 half share for each child in principal residence and 1 additional half share as a lone parent) who received taxable net income of €30,000.
His family quotient is €30,000 : 2.5 = €12,000.
- Up to €11,294 : 0%
- From €11,295 to €12,000 : (€12,000 - €11,294) x 11% = €706 x 11% = €77.66
This tax must be multiplied by the number of shares in the tax household. In this example, it will be multiplied by 2.5 since it is a lone parent with 2 children.
Please note : the tax benefit is divided by two in the case of alternate residence.
The gross tax of the family is: €77.66 x 2.5, or €194.15.
The marginal tax rate (BIT) for this family is 11%, because its family quotient puts it in that range. But not all his income is taxed to 11%.
Vous avez choisi
Choisissez votre cas
For a single man
One unmarried (household of a single share) whose net taxable income is €30,000, without any reduction or deduction.
His family quotient is €30,000.
For the calculation of his tax:
- Up to €11,294 : 0%
- From €11,295 to €28,797 : (€28,797 - €11,294) × 11% = €17,503 × 11% = €1,925.33
- From €28,798 to €30,000 : (€30,000 - €28,797) x 30% = €1,203 × 30% = €360.90
Its gross tax is: €0 + €1,925.33 + €360.90 = €2,286.23.
The marginal tax rate (BIT) of this taxpayer is 30%, because its family quotient puts it in that range. But not all his income is taxed to 30%.
For a married couple or a past couple without children
Taxable net income of €60,000
One married couple or former couple without children (household of 2 units) having received taxable net income of €60,000.
His family quotient is €60,000 : 2 = €30,000.
For the calculation of his tax:
- Up to €11,294 : 0%
- From €11,295 to €28,797 : (€28,797 - €11,294) × 11% = €17,503 × 11% = €1,925.33
- From €28,798 to €30,000 : (€30,000 - €28,797) x 30% = €1,203 × 30% = €360.90
The gross tax for each member of the couple is: €0 + €1,925.33 + €360.90 = €2,286.23.
This tax must be multiplied by the number of shares in the tax household. In this example, it will be multiplied by 2 since it is a married or a former couple.
The couple will therefore have to pay a tax of €2,286.23 × 2, or €4,572.46.
The marginal tax rate (IMR.) for this couple is 30%, because its family quotient puts it in that range. But not all his income is taxed to 30%.
Taxable net income of €90,000
One married couple or former couple without children (household of 2 units) having received taxable net income of €90,000.
His family quotient is €90,000 : 2 = €45,000.
For the calculation of his tax:
- Up to €11,294 : 0%
- From €11,295 to €28,797 : (€28,797 - €11,294) × 11% = €17,503 × 11% = €1,925.33
- From €28,798 to €45,000 : (€45,000 - €28,797) x 30% = €16,203 × 30% = €4,860.90
The gross tax for each member of the couple is: €0 + €1,925.33 + €4,860.90 = €6,786.23.
This tax must be multiplied by the number of shares in the tax household. In this example, it will be multiplied by 2 since it is a married or a former couple.
The couple will therefore have to pay a tax of €6,786.23 × 2, or €13,572.46.
The marginal tax rate (IMR.) for this couple is 30%, because its family quotient puts it in that range. But not all his income is taxed to 30%.
For a married or spent couple with 2 children
Taxable net income of €60,000
One married or past couple with 2 children (focus of 3 shares, 1 share for each parent and 1 half share for each child) who received net taxable income of €60,000.
His family quotient is €60,000 : 3 = €20,000.
For the calculation of his tax:
- Up to €11,294 : 0%
- From €11,295 to €20,000 : (€20,000 - €11,294) x 11% = €8,706× 11% = €957.66
This tax must be multiplied by the number of shares in the tax household. In this example, it will be multiplied by 3 since it is a married or past couple with 2 children.
The couple with 2 children should therefore pay a tax of: €957.66 x 3, or €2,872.98
The couple shall be entitled to a maximum tax advantage of €3,518 (€1,759 x 2) for his 2 children (it is the family quotient ceiling).
A married or non-married couple who have received a net taxable income of €60,000 will have to pay a tax of €4,572.46.
The advantage associated with the 2 children is therefore €1,699.48 (€4,572.46 - €2,872.98).
The amount of this benefit shall be less than the maximum benefit of €3,518.
The couple with 2 children will therefore have to pay a tax of €2,872.98
The marginal tax rate (BIT) for this couple with 2 children is 11%, because its family quotient puts it in that range. But not all his income is taxed to 11%.
Taxable net income of €90,000
One married or past couple with 2 children (focus of 3 shares, 1 share for each parent and 1 half share for each child) who received net taxable income of €90,000.
His family quotient is €90,000 : 3 = €30,000.
For the calculation of his tax:
- Up to €11,294 : 0%
- From €11,295 to €28,797 : (€28,797 - €11,294) × 11% = €17,503 × 11% = €1,925.33
- From €28,798 to €30,000 : (€30,000 - €28,797) x 30% = €1,203 × 30% = €360.90
The gross tax for each member of the couple is: €0 + €1,925.33 + €360.90 = €2,286.23.
This tax must be multiplied by the number of shares in the tax household. In this example, it will be multiplied by 3 since it is a married or past couple with 2 children.
The couple with 2 children should therefore pay a tax of €2,286.23 × 3, or €6,858.69.
The couple shall be entitled to a maximum tax advantage of €3,518 (€1,759 x 2) for his 2 children (it is the family quotient ceiling).
A married or non-married couple who have received a net taxable income of €90,000 will have to pay a tax of €13,572.46.
The advantage related to children is €6,713.77 (€13,572.46 - €6,858.69).
This amount exceeds the maximum tax benefit to which the couple is entitled for their 2 children of €3,195.77 (€6,713.77 - €3,518).
The couple with 2 children will therefore have to pay a tax of €10,054.46 (€6,858.69 + €3,195.77).
The marginal tax rate (BIT) for this couple with 2 children is 30%, because its family quotient puts it in that range. But not all his income is taxed to 30%.
For a single parent with 2 children
One single parent with 2 children (household of 2.5 shares, 1 share for the parent, 1 half share for each child in principal residence and 1 additional half share as a lone parent) who received taxable net income of €30,000.
His family quotient is €30,000 : 2.5 = €12,000.
- Up to €11,294 : 0%
- From €11,295 to €12,000 : (€12,000 - €11,294) x 11% = €706 x 11% = €77.66
This tax must be multiplied by the number of shares in the tax household. In this example, it will be multiplied by 2.5 since it is a lone parent with 2 children.
Please note : the tax benefit is divided by two in the case of alternate residence.
The gross tax of the family is: €77.66 x 2.5, or €194.15.
The marginal tax rate (BIT) for this family is 11%, because its family quotient puts it in that range. But not all his income is taxed to 11%.
Infographie - Income tax: 2024 schedule
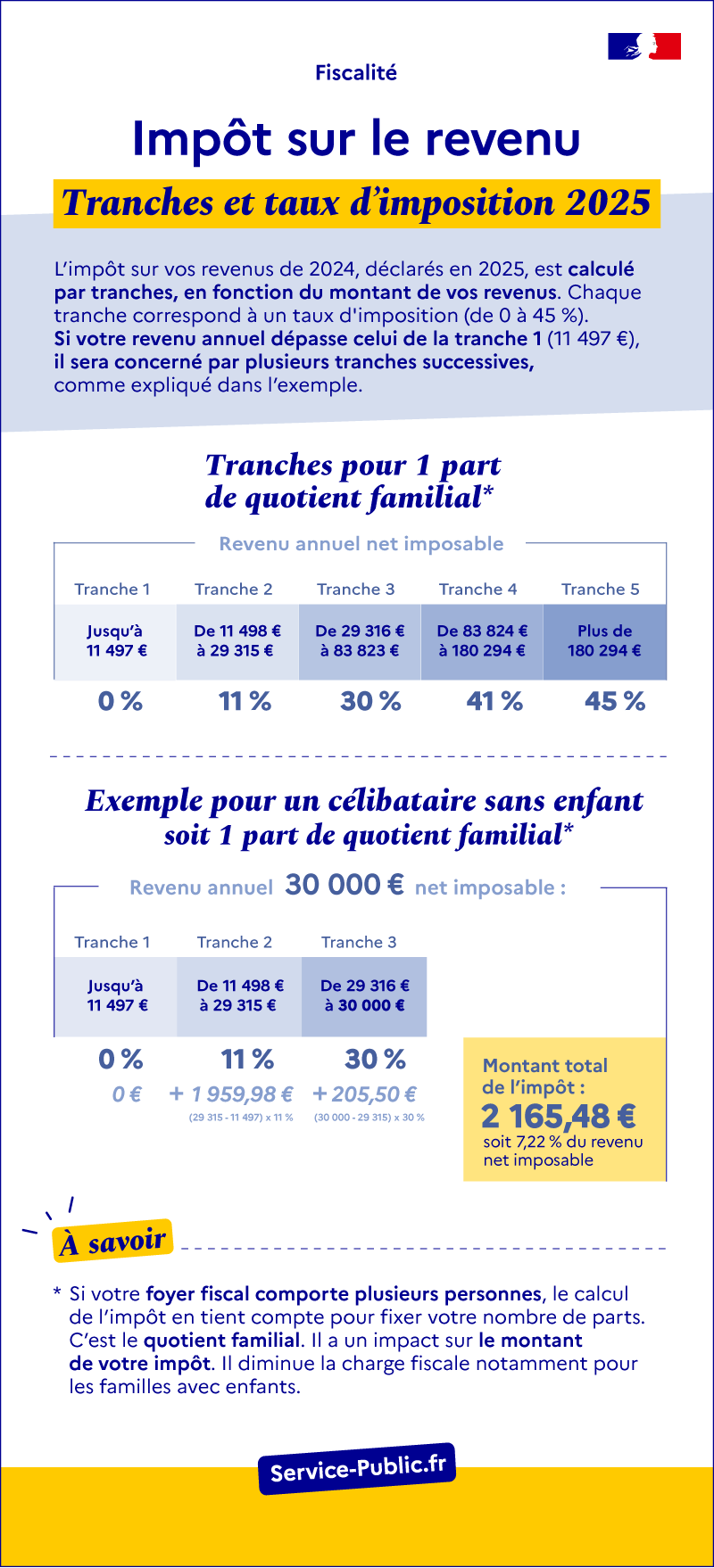
Ouvrir l’image dans une nouvelle fenêtre
Income tax
2024 tax brackets and rates
Your tax is calculated in installments, based on the amount of your income. Each bracket corresponds to a tax rate (from 0 to 45%). If your annual income exceeds that of bracket 1 (€10,777), it will be covered by several successive brackets, as explained in the example.
Slices for 1 share of family quotient:
- Up to €11,294 (bracket 1): 0% tax rate
- From €11,295 to €28,797 (bracket 2): tax rate of 11%
- From € 28 798 to € 82 341 (bracket 3): 30% tax rate
- From €82 342 to €177 106 (bracket 4): tax rate of 41%
- More than €177 106 (bracket 5): tax rate of 45%
Example of calculation for 1 share of family quotient:
A single person (1 share) whose annual net taxable income is €30,000, the calculation of his tax is as follows:
- Up to €11,294 (tranche 1): €0
- From €11 295 to €28 797 (tranche 2): €1 925.33
- From €28 798 to €30 000 (tranche 3): €360.90
Total tax: €2,286.23, or 7.62% of his net taxable income.
That is, if you have more than one person in your tax household, the tax calculation takes that into account when determining your number of shares. This is the family quotient. This mechanism has an impact on the amount of your tax. In particular, it reduces the tax burden for families with children.
The gross tax can be adjusted in certain situations.
To calculate your net tax, devices are used depending on your situation:
- Capping the effects of the family quotient
- Discount (if your income is modest)
- Reductions and tax credits
- Contribution on high income
Capping the effects of the family quotient
The tax advantage provided by the additional half-shares is capped. It can't exceed a fixed amount based on your situation.
The tax reduction related to the family quotient is limited to €1,759 for each additional half-share (€880 for each additional quarter share).
In some specific situations, the tax reduction related to the family quotient is different, for example:
- €1,050 for the half-share granted, subject to conditions, if you raised a child alone for 5 years
- €3,512 for the half-share granted if you are disabled or a veteran
Beyond the limit that corresponds to your situation, your additional half-shares (or shares) are no longer taken into account to calculate your tax amount.
Discount
The discount allows you to reduce your tax if you are taxable but your income is modest.
Répondez aux questions successives et les réponses s’afficheront automatiquement
You're single
You receive a discount if your gross income tax does not exceed €1,929.
The haircut shall be equal to the difference between €873 and 45.25% the amount of your tax.
Example :
If your gross tax is €1,400 :
€1,400 x 45.25% = €633.50
The discount is €873 - €633.50 = €239.50.
It is deducted from your tax.
The amount of tax after discount is €1,400 - €239.50 = €1,160.50.
You are a couple subject to common taxation
You receive a discount if your gross income tax does not exceed €3,191.
The haircut shall be equal to the difference between €1,444 and 45.25% the amount of your tax.
Example :
If your gross tax is €1,400 :
€1,400 x 45.25% = €633.50
The discount is €1,444 - €633.50 = €810.50.
It is deducted from your tax.
The amount of tax after discount is €1,400 - €810.50 = €589.50.
Vous avez choisi
Choisissez votre cas
You're single
You receive a discount if your gross income tax does not exceed €1,929.
The haircut shall be equal to the difference between €873 and 45.25% the amount of your tax.
Example :
If your gross tax is €1,400 :
€1,400 x 45.25% = €633.50
The discount is €873 - €633.50 = €239.50.
It is deducted from your tax.
The amount of tax after discount is €1,400 - €239.50 = €1,160.50.
You are a couple subject to common taxation
You receive a discount if your gross income tax does not exceed €3,191.
The haircut shall be equal to the difference between €1,444 and 45.25% the amount of your tax.
Example :
If your gross tax is €1,400 :
€1,400 x 45.25% = €633.50
The discount is €1,444 - €633.50 = €810.50.
It is deducted from your tax.
The amount of tax after discount is €1,400 - €810.50 = €589.50.
Reductions and tax credits
The tax reductions and credits to which you are entitled must be deducted from the amount of your tax.
For example, the donation rebate bodies of general interest.
FYI
the tax is not payable when the amount of the tax is less than €61. This is the amount after tax cuts and discounts, but before any tax credits are applied.
Exceptional contribution on high incomes
In case of high income, the exceptional contribution may be added to income tax.
Who can help me?
Find who can answer your questions in your region
For general information
Tax Information Service
By telephone:
0809 401 401
Monday to Friday from 8:30 am to 7 pm, excluding public holidays.
Free service + call price
To contact the local service managing your folder
Department in charge of taxes (treasury, tax department...)
Calculation of income tax
Amount below which the tax is not assessed (Article 1657)
FAQ
Service-Public.fr
Ministry of Finance
Ministry of Finance

